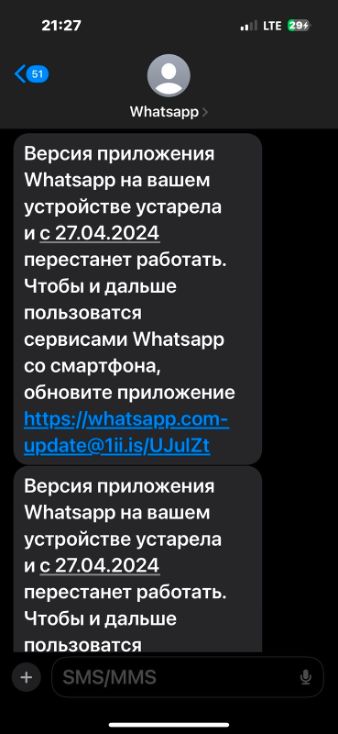
However, the URL uses a redirection service (redirec[.]fit) to navigate users to a legitimate-looking but malicious website hosted on the WP engine platform.
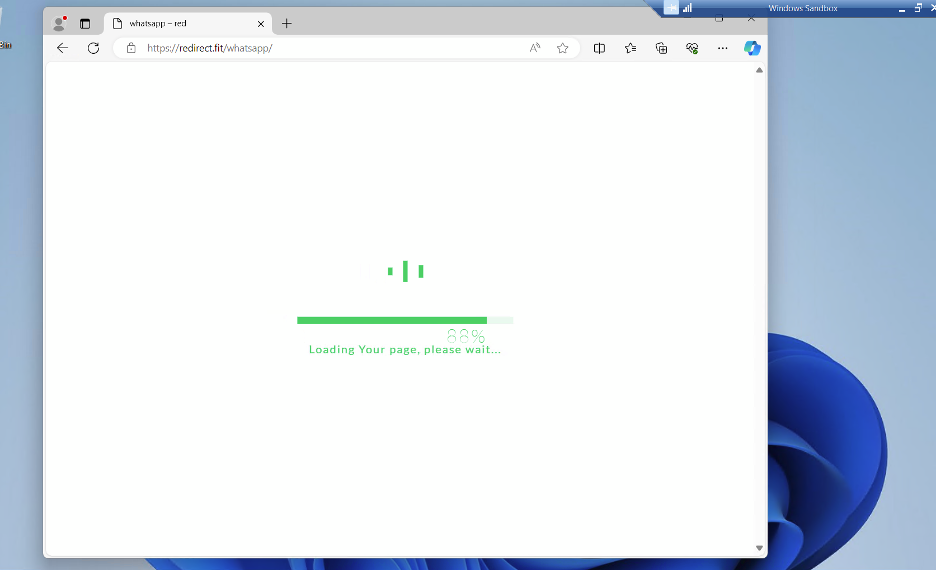
Phishing Website
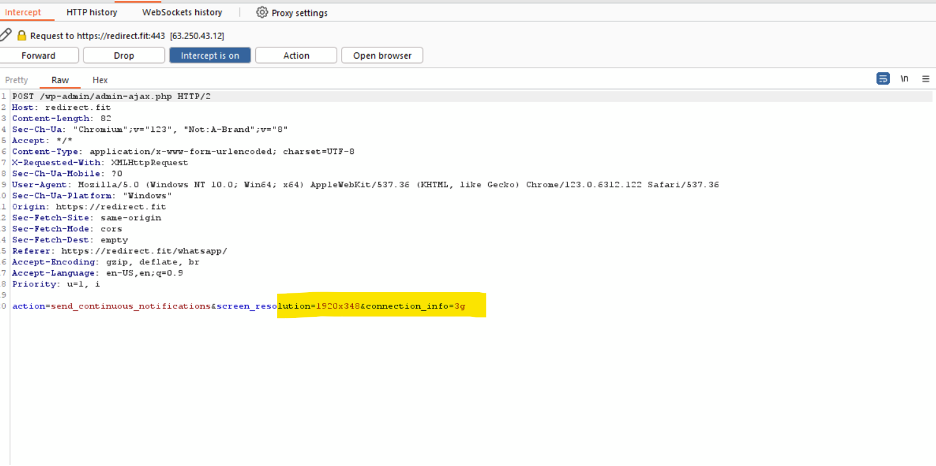
The phishing website is designed to collect user information, including connection type metadata. It is suspected that the attackers are using this website to inject phishing forms tailored to their current campaign.
Targeted Services
Based on the website’s header information, the phishing campaign appears to be targeting the following services:
- Whatsapp
- Yandex Delivery
- Adjarabet
- Yandex Music
An analysis of the injected JavaScript and other components on the phishing website did not reveal any signs of spyware or malware presence. However, it is possible that the attackers are primarily focused on collecting user information through phishing forms rather than delivering malware.
Potential Impact
Users who fall for this phishing attack and enter their information on the malicious website risk having their personal data, including login credentials, compromised. This could lead to further exploitation, such as account hijacking, identity theft, or financial fraud.
Recommendations
To protect against this threat, users should:
- Be cautious of unsolicited messages, especially those containing suspicious links or prompts to update applications.
- Verify the legitimacy of URLs by carefully inspecting the domain name and ensuring it matches the official website of the service in question.
- Keep their software and applications up-to-date through official channels and trusted sources.
- Use strong and unique passwords for their accounts, and enable two-factor authentication when available.
- Report any suspicious messages or phishing attempts to the appropriate authorities or service providers.


