Telegram’s position is quite solid in Armenia today both as a messenger, which uses encrypted chats and is considered to be safe in that sense, and as a social network and information platform, where dozens of news channels and blogs operate.
Telegram is also a platform for political recruitment, social activism, as it allows creating large chat groups, which, in its turn, makes it a target for a number of cyber-attacks.
This blog-post will present several cases, which will demonstrate the main attack vectors against Telegram users in recent months.
The first attack is directed against the administrators of Telegram channels. The hackers contact the admin from the account of an unknown Russian-speaking user offering to publish a paid advertisement on the channel. They say that they need to promote a video editing program, which is not yet available for phones and is only available as a Google Chrome extension. After the successful negotiations, they send a .rar archive file, suggesting to install the application, test it and post about it. In reality, the archive file contains an .exe file that is only 115 KB in size while compressed, but once unpacked, it expands to a 750 MB and appears to be a Trojan (the artificial size enlargement may have been done on purpose so that the file exceeds Virustotal’s upload limits, which makes it harder to scan). At the moment of the attack, only six antivirus programs detected the file as malacious. At the moment of publication the number of antivirus engines detecting it has reached eleven, but even this is a small number, given that the most common antiviruses do not detect the Trojan, including Microsoft Defender, which is installed by default in the Windows operating system. More detailed information on the Trojan can be found here.
The other attack is very subtle. A telegram user receives a phishing message, which is crafted to look exactly like Telegram’s usual warning that the account has been accessed from another device. The recipient is led to believe, that hackers have cracked his/her account. The only visible difference from Telegram’s real warning message is that it offers to visit telegram.vet, a phishing site imitating the address of Telegram’s real website.
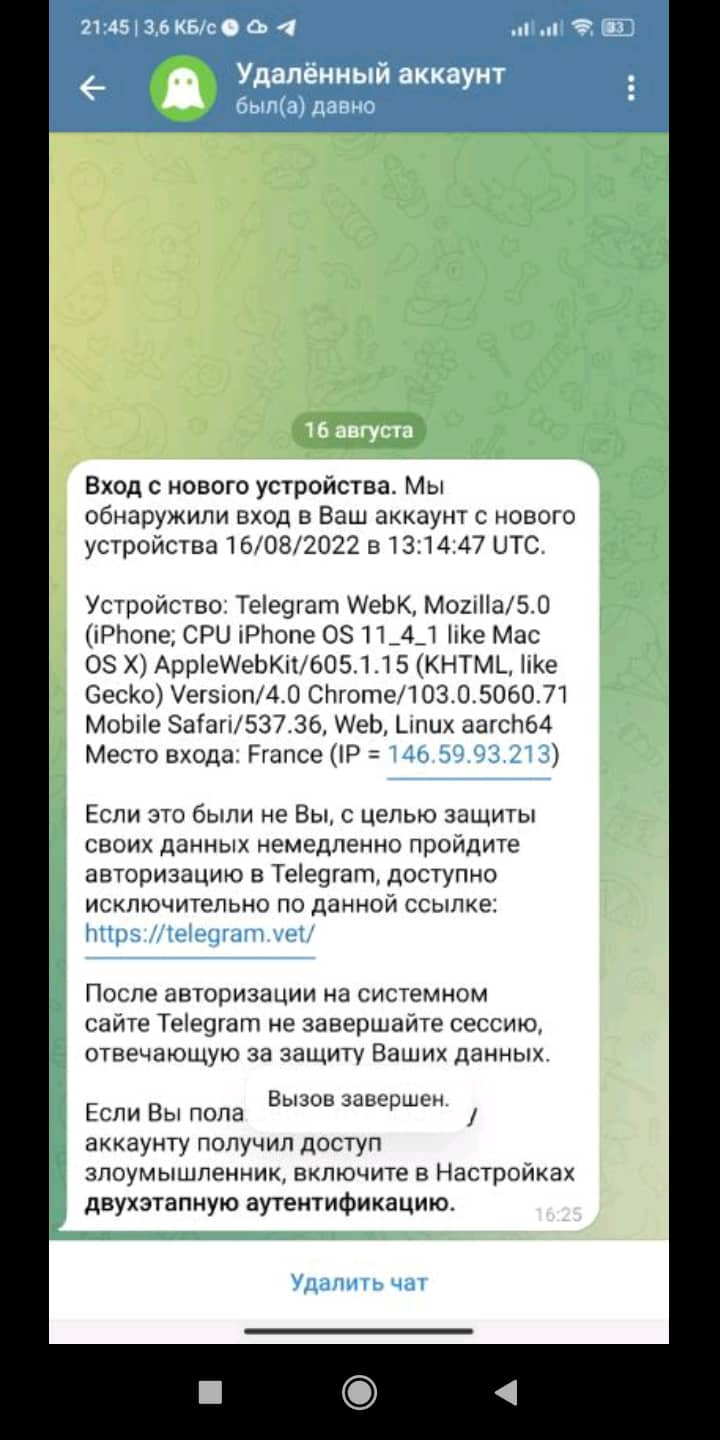
If the user is not careful, he/she can unknowingly attach his/her account to the hacker’s device using a QR code.
 Currently the mentioned phishing site is already identified as malicious by thirteen security systems, while at the moment of the attack only one saw the danger.
Currently the mentioned phishing site is already identified as malicious by thirteen security systems, while at the moment of the attack only one saw the danger.
The perpetrators of these two attacks are unknown, it is difficult to understand whether the attacks were directed against Armenia-based or Armenian targets, or whether they are related to larger scale and untargeted attacks. However, the third attack most likely is of a highly internal and political nature.
Let us take a closer look at it: cyber security expert Ruben Muradyan discovered three hacked Telegram accounts in May 2022.
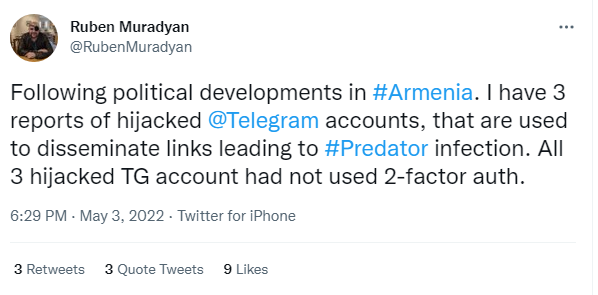
The accounts had most probably been hacked by intercepting the SMS recovery codes. None of the three hacked accounts had enabled two-step verification. A few years ago we have come acorss with hacking attacks by intercepting SMS in Armenia.
These hacked Telegram accounts were later used to disseminate the Predator spyware. It should be noted that this program was used against domestic political and media targets in Armenia, and there is a very high probability that it is linked to local special services.